Role of Blockchain in Cybersecurity
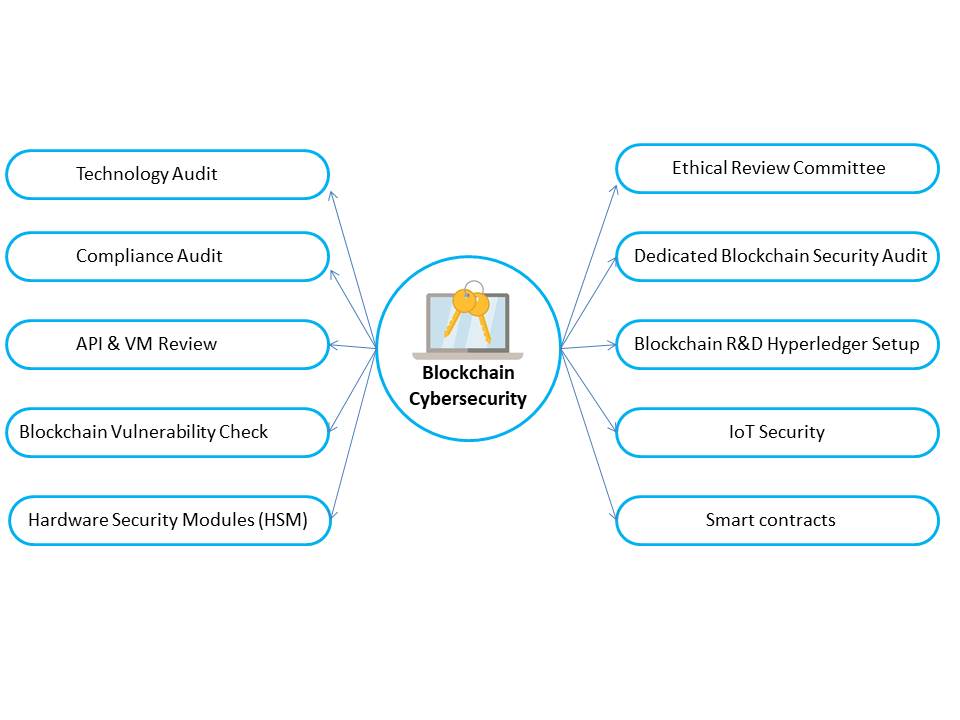
Technology Audit | Compliance Audit | API & VM Review | Blockchain Vulnerability Check | Hardware Security Modules (HSM) | Ethical Review Committe | Dedicated Blockchain Security Audit | Blockchain R&D Hyperledger Setup | IoT Security | Smart contracts
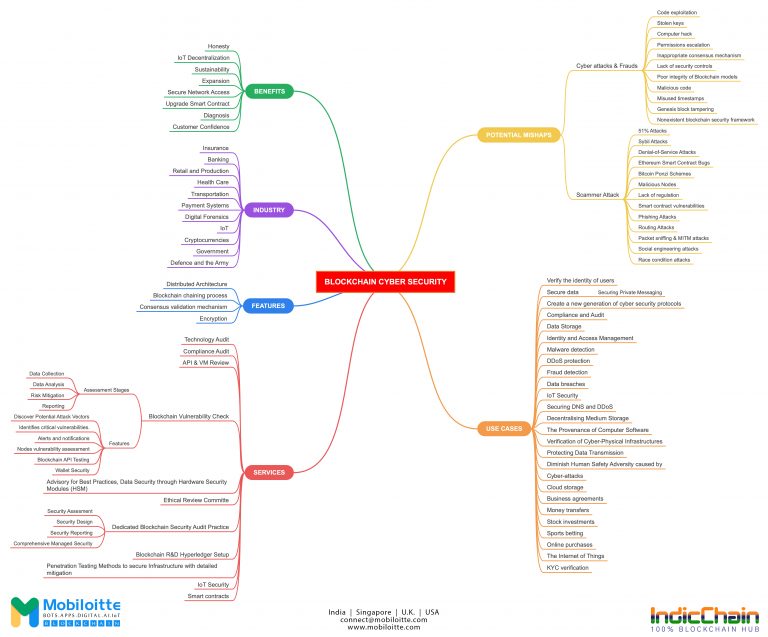
Blockchain Cybersecurity Services
Get in Touch
Enhance Cybersecurity with Blockchain
Blockchain Cybersecurity – The increasingly complex digital world we live in makes it harder to secure our systems against cyber threats, especially as criminals are encouraged to think outside the box and research new ways to exploit vulnerabilities.
Cyber security is one of the most pressing challenges facing businesses, governments and individuals. Blockchain provides a way to make our data more secure by removing centralized control, which can be manipulated. It also provides strong encryption and verification of data ownership and integrity. Finally, it can even eliminate the need for some passwords, which are frequently described as the weakest link in cyber security.
The revolutionary benefits of Blockchain technology come from its decentralized architecture and contentious roots. The distributed nature of Blockchain technology ensures that transactions are verified by different computing devices across the network, making it difficult for attackers to tamper with data or steal funds.
Mobiloitte’s solution for Blockchain Cybersecurity
Our devoted team of Blockchain Cybersecurity specialists, architects, and engineers is here to assist you in ensuring that your Blockchain implementations have safe lifecycle management. The team has demonstrated experience in a variety of areas, including safe Blockchain architecture and design, security audits, vulnerability scanning, and remedial services.
Mobiloitte’s Process
Implementing Blockchain for Cybersecurity
The Chaining Method of Blockchain
To facilitate the execution of transactions, the blocks that make up a Blockchain ledger are sorted into a specific order and then composed. A header plus a body together into what is known as a block. Each block bears a timestamp as well as the signature of the person who created it. By establishing a pointer to the block that came before it, the blocks come together to create a chain. The immutability of the most recent block is ensured by the header, which provides a cryptographic hash of the block that came before it.
Consensus Validation Methodology
The consensus process’s job is to determine whether or not newly added data blocks are legitimate. To determine if the newly added data block is legitimate and qualified for the shared ledger, a predetermined member of the nodes is required to reach a consensus. The consensus method provides for ongoing verification of the completeness of both the historical transactions and the most recent data blocks.
If a hacker wanted to alter the ledger, they would have to compromise a significant portion of nodes, hence the consensus mechanism. By putting in place an adequate number of nodes and relying on network rules to reach an agreement among those nodes, the Blockchain network contributes to the prevention of attacks of this kind.
Architecture with Distributed Components
A distributed network is robust to operational failure since there is no central point of failure in the system. Risk is spread among a number of nodes, and the ledger can withstand an assault on any one or a small number of those nodes without being corrupted. As a result, the Blockchain network is rendered a less desirable target for ransomware assaults due to its decentralized nature. The information that is kept in a centralized location is, in contrast, more vulnerable to assaults than the information that is stored at various nodes.
For a ransomware attack to be successful, it is necessary to compromise the majority or all of the network’s nodes. On the other hand, restoring full service once the nodes have been compromised won’t happen instantly; there may be some delay impacts on the recovery of the network.
Encryption
Multiple types of encryption are utilised, each at a specific degree of implementation, to offer a multi-layered defence against potential Cybersecurity risks. Asymmetric key algorithms and hash functions are examples of the types of cryptographic algorithms.
Hashes and digital signatures, both of which are based on encryption using public and private keys, are used to encrypt the linked lists and blocks, respectively.
Benefits of Blockchain Cybersecurity
The following is a list of some of the aspects that make Blockchain such exciting technology and some of the ways it should be managed:
Privacy Protection and Data Security
Administration of the Public Key Infrastructure
Smart contracts
Access control, authentication, data security, and business logic validation are some of the aspects that should be verified for Blockchain components such as smart contracts, apps, APIs, digital assets, and wallets. This results in increased levels of confidence among those who participate in the permissioned chains.
Why Mobiloitte for Blockchain Cybersecurity?
Mobiloitte provides a wide range of Blockchain-related services, including Blockchain development, DEX development, NFT development and Blockchain Cybersecurity services. You can rely on our developers to ensure the safety and integrity of your Blockchain systems with our cutting-edge solutions. Reach out to us to learn more about procedures!